High broadband growth in Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand: Akamai
By Digital News Asia October 23, 2013
- Q2 2013 is first quarter in which half of all connections occurred at 4 Mbps or higher
- Indonesia pushes China out of top spot as source of attack traffic; US remains No 3
 ACCORDING to Akamai Technologies Inc’s Second Quarter, 2013 State of the Internet Report, there were “extremely large growth rates” of broadband adoption seen in Malaysia (127%), Thailand (195%), Indonesia (292%) and China (503%), all of which more than doubled their levels of broadband adoption from the second quarter of 2012.
ACCORDING to Akamai Technologies Inc’s Second Quarter, 2013 State of the Internet Report, there were “extremely large growth rates” of broadband adoption seen in Malaysia (127%), Thailand (195%), Indonesia (292%) and China (503%), all of which more than doubled their levels of broadband adoption from the second quarter of 2012.
The most impressive growth rates were seen in Indonesia, which grew by nearly three times year-over-year, and in China, which was up over 500% during the same period, the company said in a statement.
All four countries saw yearly growth rates above 100% in the first quarter as well, so the continued aggressive growth (click Figure 27 to enlarge) in this metric is an extremely encouraging trend, Akamai said.
Akamai’s State of the Internet reports are based on data gathered from the Akamai Intelligent Platform, and provide insight into key global statistics such as network connectivity and connection speeds, attack traffic, and broadband adoption and availability, among others.
The Second Quarter, 2013 State of the Internet Report includes insights into attacks for which a group calling itself Syrian Electronic Army has claimed responsibility, as well observations on Akamai traffic activity due to Internet disruptions in Sudan and Syria.
The report also reviews mobile browser usage by network type based on data from Akamai IO.
Global average and peak connection speeds
Global average peak connection speeds increased slightly during the second quarter of 2013, up 0.1% to 18.9 Mbps. Among the top 10 countries/ regions that saw higher average peak connection speeds in the quarter, increases ranged from 3.1% in Japan (to 48.8 Mbps) to 22% in Taiwan (to 39.5 Mbps).
Hong Kong continued to maintain the No 1 ranking at 65.1 Mbps, and South Korea crossed the 50 Mbps threshold, coming in second at 53.3 Mbps. Malaysia, ranked No 44 in terms of average peak connection speeds, saw a 5.4% quarterly increase to 26.6 Mbps.
Year-over-year, global average peak connection speeds continued to demonstrate solid growth, rising 17%. Yearly growth rates among the top 10 countries ranged from 14% in South Korea to 61% in both Singapore and Taiwan.
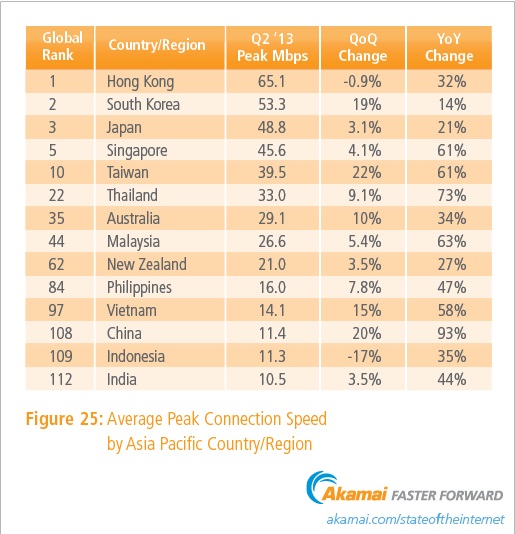 The average peak connection speeds across surveyed Asia Pacific countries/ regions were all positive in the second quarter, and exceedingly so, Akamai said (click Figure 25 to enlarge).
The average peak connection speeds across surveyed Asia Pacific countries/ regions were all positive in the second quarter, and exceedingly so, Akamai said (click Figure 25 to enlarge).
China saw the largest yearly increase, growing 93%, with Thailand, Malaysia, Taiwan, and Singapore all seeing average peak connection speeds improve by more than 60% over the prior year. Vietnam’s average peak speed grew by 58% year-over-year, while the Philippines and India saw increases above 50%, with Indonesia, Australia, and Hong Kong adding more than 30% each.
The lowest average peak connection speed increase seen over the past year occurred in South Korea, which added 14%.
Around the rest of the world, all but six qualifying countries/ regions saw yearly growth in average peak connection speeds, ranging from 8.5% in Bermuda (to 13.4 Mbps) to increases of more than 200% in Bahrain (284% to 40.3 Mbps) and Iraq (274% to 27.3 Mbps).
Quarter-over-quarter, the global average connection speed rose 5.2% to 3.3 Mbps (up from 3.1 Mbps). A total of 129 countries/ regions that qualified for inclusion saw average connection speeds increase in the second quarter, ranging from 0.1% in Bulgaria (to 6.7 Mbps) to 93% in Sudan (to 2.1 Mbps).
Year-over-year, average connection speeds were up 9.2%, with nine of the top 10 countries/ regions demonstrating positive growth of more than 10%. Worldwide, 127 qualifying countries/ regions saw a year-over-year increase in average connection speeds, ranging from 0.6% in Argentina (to 2 Mbps) to 262% in Côte d’Ivoire (to 1.6 Mbps).
Global high broadband (>10 Mbps) adoption rose to 14% thanks to a 13% quarter-over-quarter increase. Global broadband (>4 Mbps) improved 11% on the quarter, and the second quarter (Q2 2013) marked the first time that half of all connections to Akamai from around the world took place at speeds of at least 4 Mbps.
Attack traffic and security
Akamai maintains a distributed set of unadvertised agents deployed across the Internet that log connection attempts, which the company classifies as attack traffic. Based on the data collected by these agents, the company is able to identify the top countries from which attack traffic originates, as well as the top ports targeted by these attacks.
It is important to note, however, that the originating country as identified by the source IP address may not represent the nation in which an attacker resides. For example, an individual in the United States may be launching attacks from compromised systems anywhere in the world, Akamai noted.
In the second quarter, Akamai observed attack traffic originating from 175 unique countries/ regions, two fewer than was observed in the first quarter of 2013. Indonesia pushed China out of the top spot this quarter, nearly doubling its first-quarter traffic from 21% to 38%, while China moved to second at 33% (down from 34%).
The United States remained in third even after dropping to 6.9% in the second quarter from 8.3% in the first quarter (see Figure 1).

The top 10 countries/ regions generated 89% of observed attacks, up from 82% in the previous quarter. Like the first quarter, Indonesia and China again originated more than half of the total observed attack traffic.
In addition to observations on attack traffic, the State of the Internet Report includes insight into distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks based on reports from Akamai customers.
In the second quarter of 2013, Akamai customers reported 318 attacks, a 54% increase over the 208 reported in the first quarter. At 134 reported attacks, the Enterprise sector continued to be the leading target of DDoS attacks, followed by Commerce (91), Media & Entertainment (53), High Tech (23) and Public Sector (17).
Also, a group calling itself the Syrian Electronic Army claimed responsibility for several attacks against news and media companies during the second quarter of 2013. The attacks all employed similar spear-phishing tactics in which internal email accounts were compromised and leveraged to collect credentials to gain access to targets’ Twitter feeds, RSS feeds and other sensitive information.
Mobile connectivity
During the second quarter of 2013, average connection speeds on surveyed mobile network operators ranged from a high of 9.7 Mbps to a low of 0.5 Mbps. Eleven operators demonstrated average connection speeds in the broadband (>4 Mbps) range, and 62 operators showed average connection speeds above 1 Mbps.
Data collected by Ericsson shows that the volume of mobile data traffic grew 14% during the quarter and nearly doubled year-over-year.
Based on data derived from Akamai IO for the second quarter of 2013, mobile devices on cellular networks using the Android Webkit accounted for slightly less than 38% of requests while Apple Mobile Safari saw nearly 34% of requests.
In measuring mobile devices across all network types, Apple Mobile Safari accounted just more than 54% of usage while Android Webkit was responsible for 27.6%.
To download a PDF of the Second Quarter, 2013 State of the Internet Report, click here.
Related Stories:
Asia Pacific leading broadband race, according to Akamai report
State of the Internet: Malaysia lags Thailand, but improving
For more technology news and the latest updates, follow @dnewsasia on Twitter or Like us on Facebook.


