Juniper: Mobile threats more rampant as attackers become more ‘entrepreneurial’
By Digital News Asia July 10, 2013
- Malware writers increasingly behaving like profit-motivated businesses
- 92% of all threats detected by Juniper directed at the Android operating system
 JUNIPER Networks has released its third annual Mobile Threats Report, showing the rapid growth and evolution of mobile malware into a profitable business for attackers.
JUNIPER Networks has released its third annual Mobile Threats Report, showing the rapid growth and evolution of mobile malware into a profitable business for attackers.
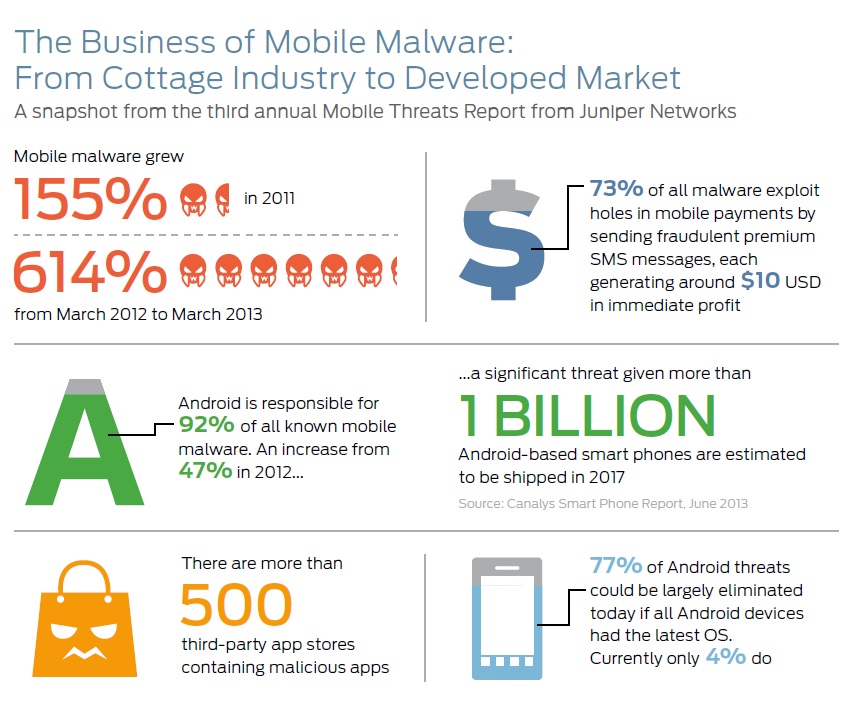
From March 2012 through March 2013, the Juniper Networks Mobile Threat Centre (MTC) – a global research facility dedicated to around-the-clock mobile security and privacy research – found mobile malware threats growing at a rapid rate of 614% to 276,259 total malicious apps, demonstrating an exponentially higher cyber criminal interest in exploiting mobile devices.
Additionally, it is clear from developments in the threat landscape that malware writers are increasingly behaving like profit-motivated businesses when designing new attacks and malware distribution strategies, Juniper Networks said in a statement.
Attackers are maximising their return on investment by focusing 92% of all MTC-detected threats at the Android operating system, which has a commanding share of the global smartphone market.
According to analyst firm Canalys, Android devices accounted for 67.7% of all smartphones shipped in 2012.
Attackers are also leveraging loosely regulated third-party app marketplaces to distribute malware and more quickly get threats on the market.
“There’s no doubt mobility will continue to be a pervasive and disruptive force across every industry,” said Troy Vennon, director of Juniper Networks’ Mobile Threat Centre.
“We have found that it has created an easy business opportunity for malware developers who are becoming savvy in their approach to quickly turn profits in a rapidly growing market. We anticipate that similar to the evolution of PC-based threats, mobile attacks will continue to increase and become more sophisticated in the coming years.”
Report highlights
This year’s MTC report uncovered several mobile malware trends that demonstrate increased business savvy by attackers including:
- Preying on high-growth market opportunities: Mobile malware developers are recognising huge opportunity in the growing market dominance of Android. Malware for the Android operating system has increased at a staggering rate since 2010, growing from 24% of all mobile malware that year to 92% by March 2013.
- More effective distribution: Attackers made strides to shorten the supply chain and find more agile methods to distribute their wares into the wild around the globe. The MTC identified more than 500 third-party Android application stores worldwide, most with very low levels of accountability or oversight, that are known to be hosting mobile malware – preying on unsuspecting mobile users as well as those with jail-broken iOS mobile devices. Of the malicious third-party stores identified by the MTC, three out of five originate from either China or Russia.
- Multiple paths to big profits: Almost three-fourths (73%) of all known malware are FakeInstallers or SMS Trojans, which exploit holes in mobile payments to make a quick and easy profit. These threats trick people into sending SMS messages to premium-rate numbers set up by attackers. Based on research by the MTC, each successful attack instance can yield approximately US$10 in immediate profit. The MTC also found that more sophisticated attackers are developing intricate botnets and targeted attacks capable of disrupting and accessing high-value data on corporate networks.
- Exploiting industry fragmentation: The fragmented Android ecosystem keeps the vast majority of devices from receiving new security measures provided by Google, which could leave users exposed to even known threats. According to Google, as of June 3, 2013, only 4% of Android phone users were running the latest version of the operating system, which provides mitigation against the most popular class of malware measured by the MTC that makes up 77% of Android threats.
- Increasing privacy violations: In addition to malicious apps, Juniper Networks found several legitimate free applications that could pose a risk of leaking corporate data on devices. Juniper Networks found free mobile applications sampled by the MTC are three times more likely to track location and 2.5 times more likely to access user address books than their paid counterparts. Free applications requesting/gaining access to account information nearly doubled from 5.9% in October 2012 to 10.5% in May 2013.
Juniper Networks said its Mobile Threats Report is based on analysis of more than 1.85 million mobile applications and vulnerabilities, up more than 133% from the last report released in February 2012.
For an executive summary of the report, click here. To read the full report (registration required), click here.
Related Stories:
The coming of BYOD and its challenges
10 tips for companies to prevent mobile malware
As mobile usage grows, so should security: IDC
Symbian malware disappearing, Android malware surges: F-Secure report
For more technology news and the latest updates, follow @dnewsasia on Twitter or Like us on Facebook.


